Contact Dr. Lu for information about cancer treatments。聯繫盧博士,獲取有關癌症治療資訊。
中国大学医院建议大剂量维生素C治疗冠状病毒感染 Chinese University Hospital recommends high doses of vitamin C to treat coronavirus infection
Contact Dr. Lu for information about cancer treatments。聯繫盧博士,獲取有關癌症治療資訊。
On the afternoon of February 20, 2020, another 4 patients with severe coronavirus induced pneumonia recovered from the C10 West Ward of Tongji Hospital in the Tongji Hospital, which was taken over by the Second Aid National Medical Assistance Team of Xi’an Jiaotong University. The medical team was formally put into work10 In the past 8 patients have been discharged from hospital.
After 10 days of practical exploration by the medical team and repeated discussions by the expert group, our expert group proposed a specific plan for the combination of high-dose vitamin C to treat the new crown, and achieved good results in clinical applications. Our treatment plan is generally summarized as “early, adequate, short course, combined.”
Early stage: The so-called “early stage” refers to the timely application of high-dose vitamin C in the early stages of the disease course. We believe that for patients with severe neonatal pneumonia and critically ill patients, vitamin C treatment should be initiated as soon as possible after admission. This is because no matter the past Keshan disease, SARS and Middle East respiratory syndrome, or the current new pneumonia, the main cause of death of patients is cardiopulmonary failure caused by increased acute oxidative stress. When the virus causes increased oxidative stress in the body and increased capillary permeability, early application of large doses of vitamin C can have a strong antioxidant effect, reduce inflammatory responses, and improve endothelial function.
Adequate: Adequate refers to the large amount of vitamin C. Numerous studies have shown that the dose of vitamin C has a lot to do with the effect of treatment. Our past experience in successfully rescuing acute Keshan disease and current studies at home and abroad show that high-dose vitamin C can not only improve antiviral levels, but more importantly can prevent and treat acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress (ARDS) .
Short-term: Short-term means that the medication time does not exceed 1 week. Short-term application of large doses of vitamin C in the critical period of disease progression can achieve twice the result with half the effort, and can significantly reduce the side effects such as kidney stones, hematuria and renal colic that should be brought in the long term, reduce nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia, etc. Adverse reactions to avoid the body’s dependence on exogenous vitamin C caused by long-term medication.
Combination: Combination refers to the combination of other treatment methods in the treatment process to develop individualized treatment plans. New crown pneumonia treatment is still without specific drugs. In the just-released “New Crown Pneumonia Diagnosis and Treatment Program Sixth Edition”, it is recommended that active symptomatic treatment be based on early trials of antiviral therapy and oxygen therapy. Therefore, the clinical application of high-dose vitamin C must be combined with the patient’s situation and combined with other drugs and treatment methods, so that it is expected to improve the treatment of critically ill patients.
In addition, when using this regimen, it should be noted that due to the high concentration, it may irritate the blood vessels and cause pain. It is recommended that isotonic fluids be given to flush the blood vessels quickly after administration to reduce the irritation of the blood vessels. In addition, we use intermittent and slow administration. Helps maintain the effective concentration of blood vitamin C, and can also reduce the local stimulation of blood vessels to the greatest extent. Finally, because vitamin C may interfere with blood glucose monitoring results, patients with diabetes should avoid measuring blood glucose immediately after infusion.
Finally, based on the various pharmacological properties of vitamin C, this treatment should not be used in patients with the following clinical conditions: 1. Allergy to vitamin C; 2. Life expectancy less than 24h; pregnant and / or lactating women; tracheotomy Have or have a family history of oxygen therapy; 6. Interstitial lung disease, malignancy, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, diabetic ketoacidosis, or a history of active kidney stones. (Translated from press release with google translate)
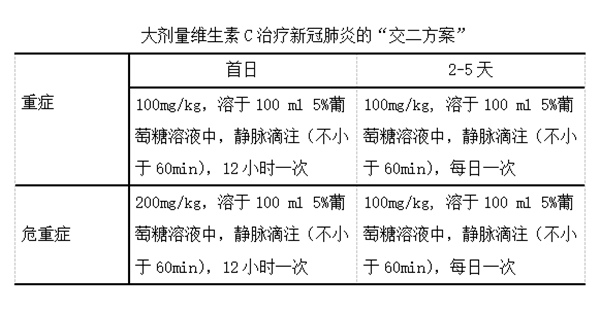
Jiao II protocol for treating severe coronavirus induced pneumonia.
For Severe cases, on day 1, the amount of vitamin C, equivalent to 100 mg/kg body weight dissolved in 100ml of 5% glucose solution for intravenous dripping that lasts for more than 60 minutes. Twice a day. On day 2 through day 5, the same solution was used in the same dripping rate once a day.
For life-threatening cases, on day 1, the vitamin C dose should be sufficient to provide 200 mg/kg for the first 12 hours, and repeat the dripping for the second 12 hours. On day 2 through day 5, the solution delivering vitamin C at the level of 100 mg/kg is used in the same dripping rate once a day.
大剂量维生素C治疗新冠肺炎的交二方案
2020年2月20日下午,由西安交通大学第二附属国家援鄂医疗队接管的同济医院中法新城院区C10西病区又有4位重型新冠肺炎患者康复出院,医疗队正式投入工作10天来,已有8位患者康复出院。
经过医疗队10天的实践探索和专家组多次讨论,我们专家组提出联合大剂量维生素C治疗新冠的具体方案,并在临床应用中取得良好的效果。我们的治疗方案总体来说概括为 “早期,足量,短程,联合”。
早期:所谓“早期”,是指大剂量维生素C应在病程发展的早期及时应用。我们认为对于新冠肺炎重症及危重症患者应在入院后第一时间启动维生素C治疗方案。这是因为不管是过去的克山病、SARS和中东呼吸综合征,还是现在的新冠肺炎,患者致死的主要原因都是急性氧化应激增加所致的心肺功能衰竭。当病毒导致机体氧化应激增加,毛细血管通透性增加时,早期应用大剂量维生素C可以起到强有力的抗氧化作用,减少炎症反应,改善内皮功能。
足量:足量是指维生素C的用量要大。大量研究表明维生素C的剂量与治疗效果有很大关系。我们既往成功抢救急性克山病的经验及目前国内外研究表明,大剂量维生素C不仅可提高抗病毒水平,更重要的是能够预防和治疗急性肺损伤(ALI)和急性呼吸窘迫症(ARDS)。
短程:短程是指用药时间不超过1周。病程进展关键时期短期应用大剂量维生素C可以达到事半功倍的作用,并可明显减少长期应有所带来的肾结石、血尿及肾绞痛等副作用,降低恶心、呕吐、低血压、心动过速等不良反应,避免长程用药所造成的机体对外源性维生素C的依赖。
联合:联合是指在治疗过程中应联合其他治疗手段,制定个体化治疗方案。新冠肺炎治疗目前仍无特效药物,在刚刚公布的《新冠肺炎诊疗方案第六版》中,建议在早期试行抗病毒治疗及氧疗的基础上,积极对症治疗。因此大剂量维生素C的临床应用一定要结合患者情况,联合其他药物及治疗手段,这样才有望提高重危患者的救治水平。
此外在应用该方案治疗时应注意由于浓度较高,故可能刺激血管引起疼痛,建议给药后给予等渗液快速冲洗血管,减轻对血管的刺激,另外我们采用间断缓慢给药的方式不但有助于维持血维生素C的有效浓度,另外可以最大程度降低了给药对血管局部的刺激。最后因为维生素C可能会干扰血糖监测结果,对于糖尿病患者应避免在输注即刻测定血糖。
最后基于维生素C的各种药理学特性,临床上存在以下情况的患者不宜使用这种治疗方案:1.对维生素C过敏;2.预期寿命不到24h;怀孕和/或哺乳期妇女;气管切开或有家庭氧疗病史;6. 间质性肺病、恶性肿瘤、弥漫性肺泡出血、糖尿病酮症酸中毒或活动性肾结石病史。